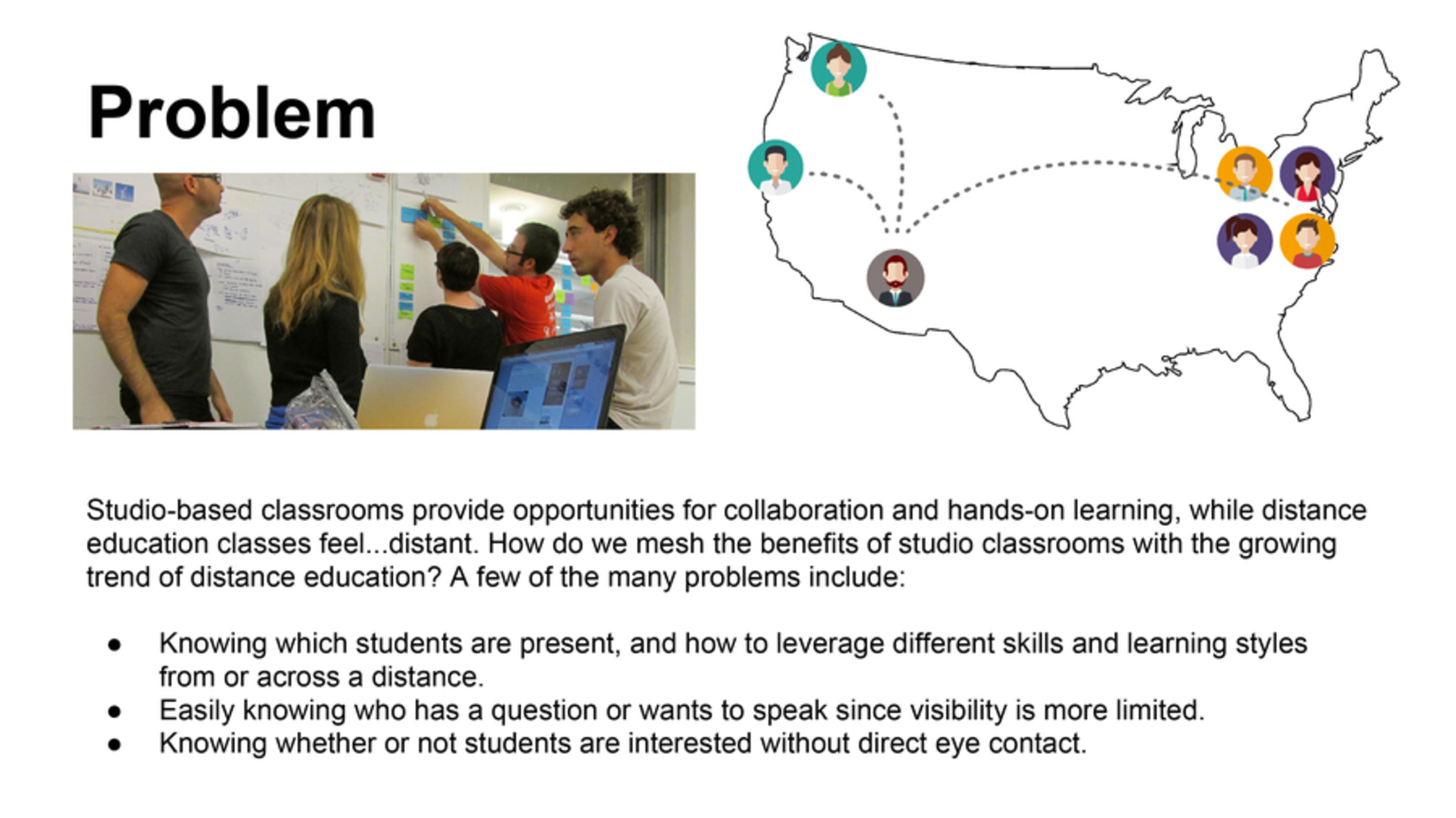
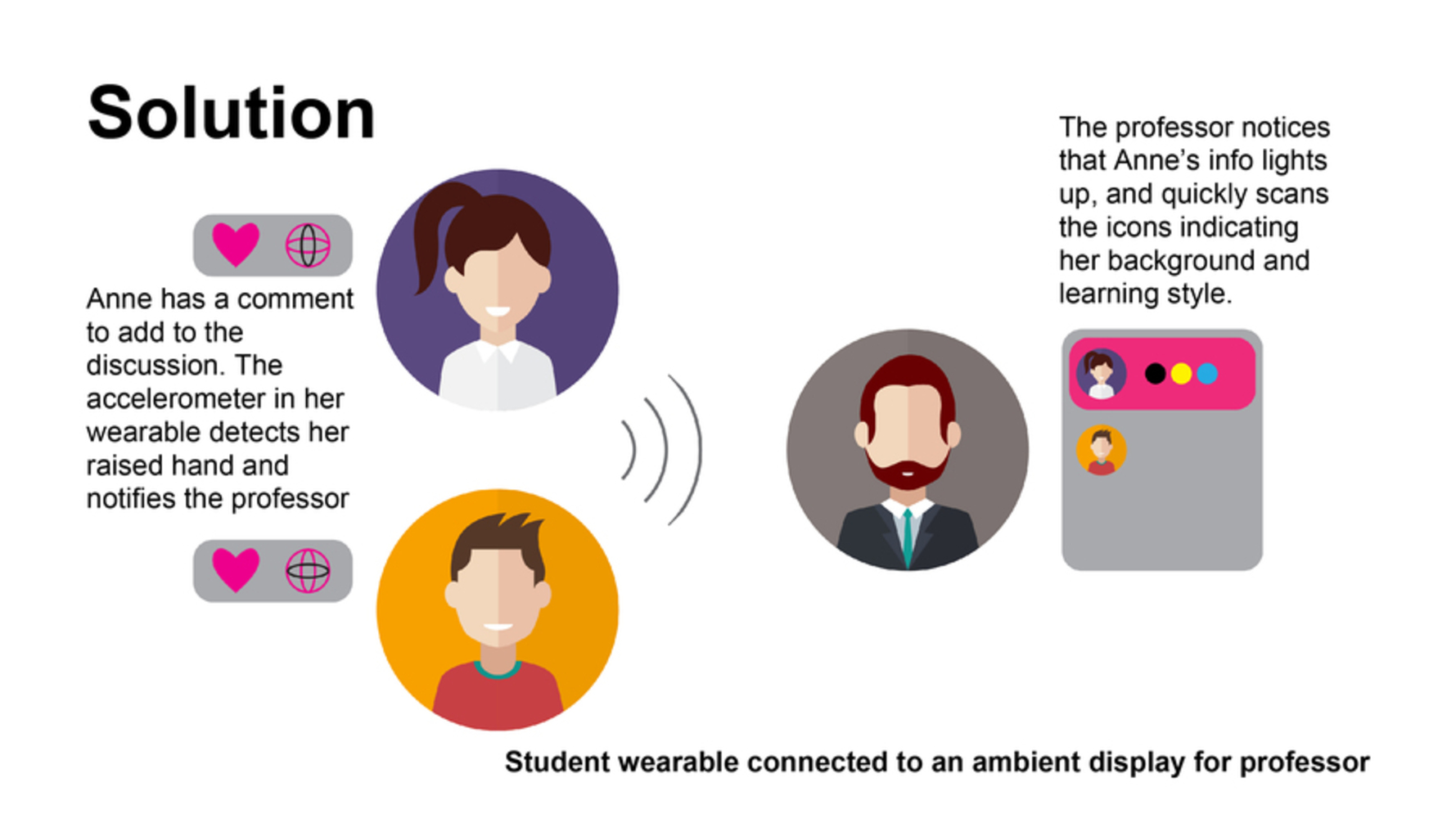
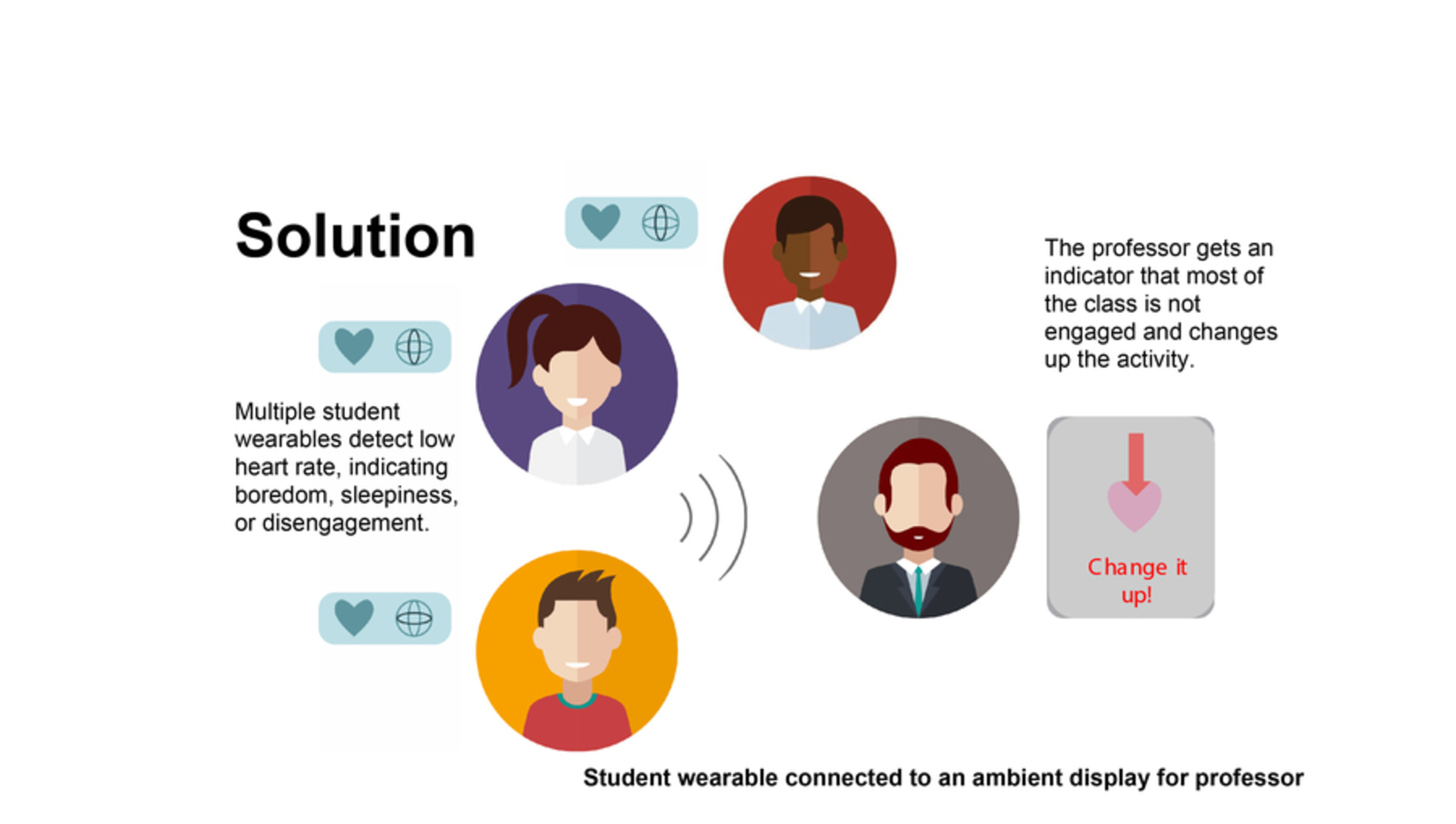
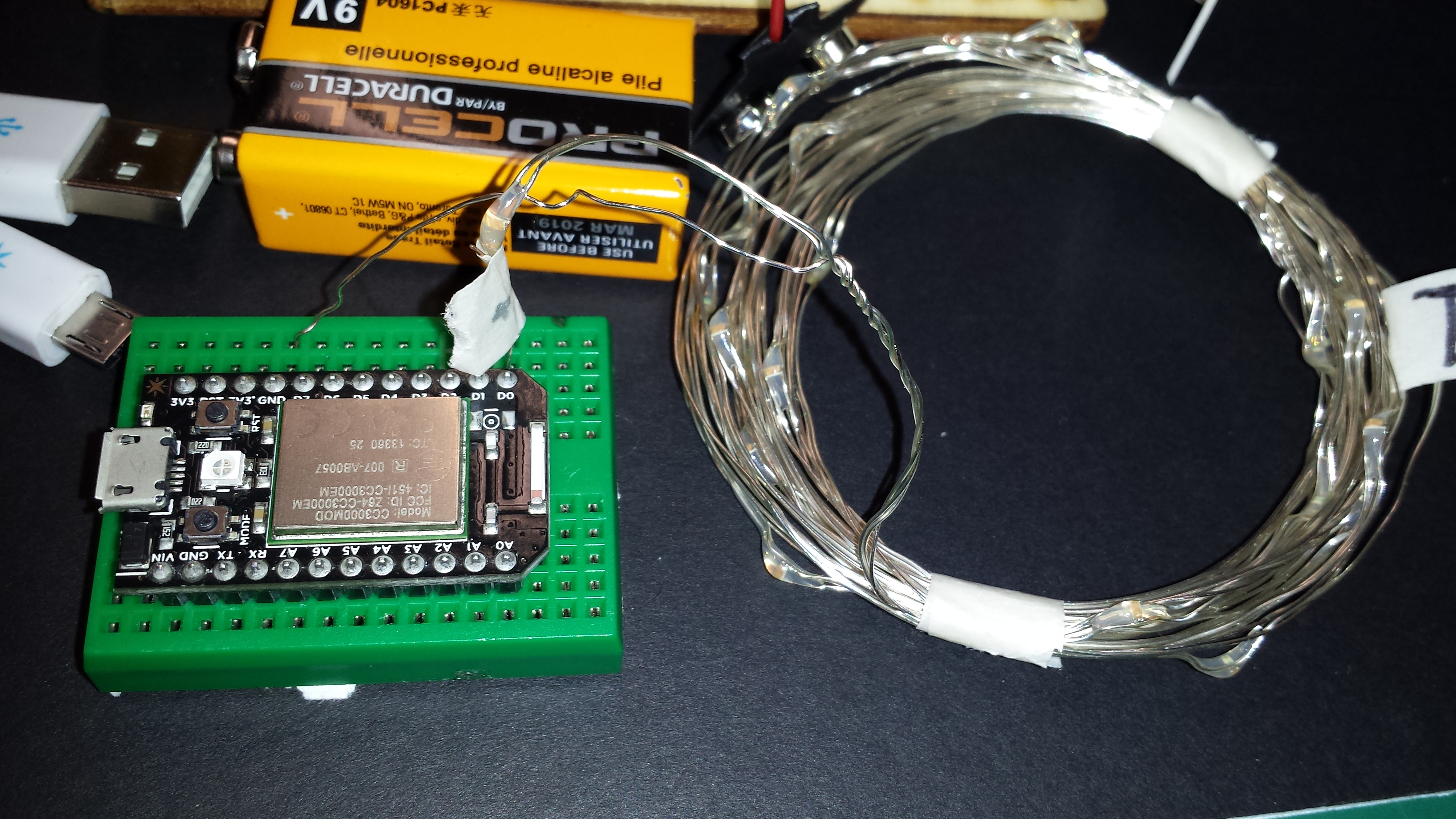
Studio-based classrooms provide opportunities for collaboration and hands-on learning, while distance education classes feel...distant. How do we mesh the benefits of studio classrooms with the growing trend of distance education? A few of the many problems include: - Knowing which students are present, and how to leverage different skills and learning styles from or across a distance. - Easily knowing who has a question or wants to speak since visibility is more limited. - Knowing whether or not students are interested without direct eye contact.
Created: March 4th, 2015
Share this Project
About
Studio-based classrooms provide opportunities for collaboration and hands-on learning, while distance education classes feel...distant. How do we mesh the benefits of studio classrooms with the growing trend of distance education? A few of the many problems include:
- Knowing which students are present, and how to leverage different skills and learning styles from or across a distance.
- Easily knowing who has a question or wants to speak since visibility is more limited.
- Knowing whether or not students are interested without direct eye contact.